➔ Calculate Head Loss
➔ Calculate Static Head Z1
➔ Calculate Pressure P1
➔ Calculate Velocity V1
Bernoulli Theorem Calculators
Bernoulli's Theorem relates the pressure, velocity, and height (static head) of a flowing fluid. It is expressed as:
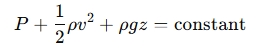
Where:
- is the pressure at the point (Pa),
- is the fluid density (kg/m³),
- is the velocity at the point (m/s),
- is the acceleration due to gravity (9.81 m/s²),
- is the height or elevation (m),
- The constant represents the total energy per unit volume.
Now, Bernoulli's theorem can be applied to calculate different quantities, such as head loss, static head, pressure, or velocity. Here's how you can calculate each one:
1. Calculate Head Loss
Head loss is the energy lost due to friction or turbulence in the fluid, often caused by resistance in pipes, bends, or valves. It can be calculated using the Darcy-Weisbach equation or simplified forms in Bernoulli's equation. If we assume the equation involves two points (1 and 2), the head loss hLh_L can be calculated as:
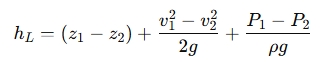
Where:
- hL is the head loss,
- z1,z2 are the heights at points 1 and 2,
- v1,v2 are the velocities at points 1 and 2,
- P1,P2 are the pressures at points 1 and 2.
2. Calculate Static Head Z1
The static head Z1 is the height of the fluid at point 1. It can be calculated using Bernoulli’s principle if the other quantities are known. Using the simplified form between two points:
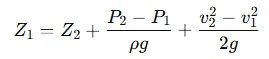
Where:
- Z1 is the static head at point 1,
- Z2 is the static head at point 2.
3. Calculate Pressure P1
The pressure at a specific point can be calculated using Bernoulli's equation rearranged:
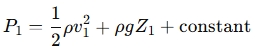
Or by using the pressure difference between two points:

Where:
- P1 is the pressure at point 1.
4. Calculate Velocity V1
The velocity at a specific point can be calculated using Bernoulli's equation rearranged:
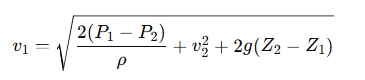
Where:
- v1 is the velocity at point 1.
Example Calculation:
If you provide values for pressure, velocity, height, or any other relevant parameters at different points in your system, I can assist in calculating one of the above parameters using Bernoulli's Theorem.