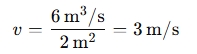➔ Calculate Flow Rate
➔ Calculate Flow Area
➔ Calculate Flow Velocity
Continuity Equation Calculators
The Continuity Equation is used in fluid dynamics to relate the flow rate, cross-sectional area, and velocity of a fluid in a pipe or conduit. The equation is:
Q=A⋅vWhere:
- is the flow rate (volume per time, e.g., m³/s),
- is the cross-sectional area (m²),
- is the flow velocity (m/s).
You can use the continuity equation to calculate any of the three variables as long as the other two are known. Here's how:
1. Calculate Flow Rate (Q)
If you know the cross-sectional area AA and the flow velocity vv, you can calculate the flow rate:
Q=A⋅vExample: If the area is 2 m² and the velocity is 3 m/s, the flow rate is:
Q=2 m2⋅3 m/s=6 m3/s2. Calculate Flow Area (A)
If you know the flow rate and the flow velocity vv, you can calculate the cross-sectional area:
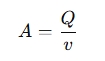
Example: If the flow rate is 6 m³/s and the velocity is 3 m/s, the flow area is:
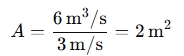
3. Calculate Flow Velocity (v)
If you know the flow rate and the cross-sectional area , you can calculate the flow velocity:
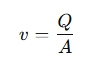
Example: If the flow rate is 6 m³/s and the area is 2 m², the velocity is: