Dynamic Head Calculator
A dynamic head calculator helps determine the total energy (head) in a fluid system caused by both elevation changes and the energy losses due to friction. It's essential in fluid dynamics and hydraulics, particularly when designing piping systems, pumps, and other fluid transport systems.
Dynamic Head Formula:
The dynamic head in a system is calculated by considering both the static head (elevation difference) and the friction head loss (energy lost due to resistance in pipes). The dynamic head (HD) is the sum of these two components.
HD=Hs+HfWhere:
- HD= Dynamic Head (total head in meters or feet)
- Hs= Static Head (difference in elevation between the fluid source and the discharge point)
- Hf= Frictional Head Loss (due to resistance in the pipe)
1. Static Head (H_s):
This is the vertical distance between the fluid source (reservoir, tank, etc.) and the discharge point (outlet). It's given by:
Hs=z1−z2Where:
- z1 = Elevation of the fluid source (in meters or feet)
- z2 = Elevation of the discharge point (in meters or feet)
2. Friction Head Loss (H_f):
The friction head loss is the energy lost due to the resistance of the fluid moving through the piping system. It depends on factors such as pipe length, pipe diameter, fluid type, flow rate, and pipe roughness.
The Darcy-Weisbach equation is commonly used to calculate the friction head loss:
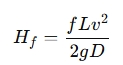
Where:
- f = Friction factor (dimensionless, depends on the pipe material and flow regime)
- L = Length of the pipe (meters or feet)
- v = Velocity of fluid in the pipe (meters per second or feet per second)
- g = Acceleration due to gravity (9.81 m/s²)
- D = Diameter of the pipe (meters or feet)
Alternatively, friction loss can be calculated using empirical charts or formulas such as the Hazen-Williams equation for water systems.