➔ Calculate Spring Index
➔ Calculate Total Shear Stress
➔ Calculate Spring Axial Deflection
➔ Calculate Spring Rate
Helical Spring Calculators
It looks like you're interested in helical spring calculations. Here’s a quick rundown on how each of those calculations work and what you’d typically need to compute them:
-
Spring Index: The spring index (C) is the ratio of the spring's mean diameter (D) to the wire diameter (d). It gives an idea of the spring’s form and is typically used to ensure that the spring is within reasonable limits for stress and fatigue.
Formula:
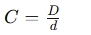
Where:
- = Mean diameter of the spring
- = Diameter of the wire
-
Total Shear Stress: The total shear stress in a helical spring is affected by the load, the geometry of the spring, and material properties. This is usually calculated using a modified version of the formula for torsional stress.
Formula:
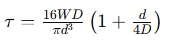
Where:
- = Load applied to the spring
- = Mean diameter of the spring
- = Wire diameter
- = Shear stress
-
Spring Axial Deflection: This refers to how much a spring deforms under an axial load. The formula for deflection depends on the material’s modulus of elasticity (E), the number of active coils (n), and the load applied to the spring.
Formula:
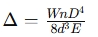
Where:
- = Load applied to the spring
- = Number of active coils
- = Mean diameter of the spring
- = Wire diameter
- = Modulus of elasticity of the material
- = Axial deflection
-
Spring Rate: The spring rate is a measure of the stiffness of the spring, indicating how much it deforms under a given load. It's calculated as the ratio of the load to the deflection.
Formula:
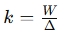
Where:
- = Load applied to the spring
- = Axial deflection