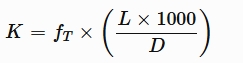
fT = Turbulent Friction Factor L = Length
D = Pipe Diameter K = K Value
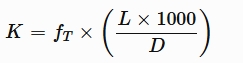
To calculate the frictional losses in a pipe due to fluid flow, we often need to determine the K value and the length of the pipe. The K value represents the pipe's resistance to flow, and it is related to the frictional losses in the system.
The K value is typically used for calculating pressure drop due to pipe fittings, valves, or other components, but it is often used in the Darcy-Weisbach equation for pipe flow:
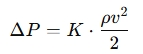
Where:
For pipes, the K value can be estimated based on:
The length of the pipe impacts the total head loss in the system due to friction. Using the Darcy-Weisbach equation for calculating head loss:
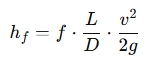
Where:
The friction factor depends on whether the flow is laminar or turbulent and can be estimated using the Colebrook equation for turbulent flow:
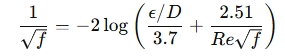
Where:
To calculate the K value and pipe length, you'll need: