➔ Calculate Head Loss
➔ Calculate Velocity
➔ Calculate Loss Coefficient
Minor Losses Equation Calculators
The Minor Losses in fluid flow through pipes refer to the losses that occur due to fittings, valves, bends, and other pipe components, in addition to the friction losses in the pipe itself. These losses are typically quantified using the minor loss coefficient (K).
Here’s how you can use the minor losses equation to calculate different parameters:
Minor Loss Equation:
The general equation for minor losses is:
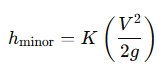
Where:
- hminor = minor head loss (meters)
- = loss coefficient (dimensionless, depends on the type of fitting, valve, etc.)
- = flow velocity (meters per second)
- = acceleration due to gravity (9.81 m/s²)
1. Calculate Head Loss ( hminorh )
To calculate the minor head loss, you would use the formula above, provided you know the loss coefficient and the flow velocity .
Example: If you have a valve with a loss coefficient of 3.5 and a flow velocity of 2 m/s, the minor head loss would be:
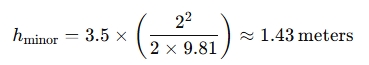
2. Calculate Velocity ( )
If you need to calculate the velocity from the minor head loss equation, you can rearrange the formula:
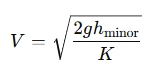
Example: If the minor head loss is 1.43 meters and the loss coefficient is 3.5, you can calculate the velocity as follows:
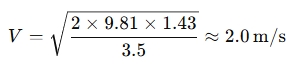
3. Calculate Loss Coefficient ( )
To find the loss coefficient , you can rearrange the equation:
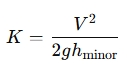
Example: If you know the velocity is 2 m/s and the minor head loss is 1.43 meters, the loss coefficient would be:
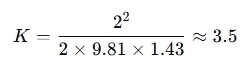
Common Values for :
The loss coefficient depends on the type of pipe fitting, valve, or other component. Here are some typical values:
- 90° Elbow: K≈0.75 to 1.5
- Gate Valve (fully open): K≈0.2
- Ball Valve (fully open): K≈0.04
- Pipe Expansion/Contraction: Kvaries significantly depending on the change in pipe diameter.