M = ( 2 x P x L ) / ( 2 x b x d2 )
M = Modulus Of Rupture
P = Breaking Load
L = Distance Between Knife Edges on which the Sample is Supported
b = Average Specimen Breadth
d = Average Specimen Depth
Modulus Of Rupture Calculator
A Modulus of Rupture (MOR) is a measure of the flexural strength of a material, specifically how much bending stress a material can withstand before it fractures. It's commonly used for materials like concrete, wood, or other building materials. The Modulus of Rupture is essentially the stress at the point of failure when a beam (or another sample) is subjected to bending.
Formula for Modulus of Rupture:
The general formula for the Modulus of Rupture (MOR) in bending is:
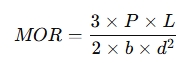
Where:
- P = Maximum load applied to the beam (N or lb)
- L = Length of the span of the beam (m or ft)
- b = Width of the beam (m or ft)
- d = Depth (thickness) of the beam (m or ft)
This formula is for a simple beam with a point load applied at the center. The Modulus of Rupture is typically expressed in MPa (megapascals) or psi (pounds per square inch), depending on the units used.
Steps to Calculate the Modulus of Rupture:
-
Determine the Material Properties: You need the material's maximum load (P), the dimensions of the beam (width and depth), and the span length.
-
Use the Formula: Plug these values into the formula to calculate the MOR.
Example Calculation:
Assume you have a wooden beam with the following dimensions:
- Length (L) = 3 meters
- Width (b) = 0.05 meters (5 cm)
- Depth (d) = 0.1 meters (10 cm)
- Maximum Load (P) = 1,200 N (newtons)
Using the formula:
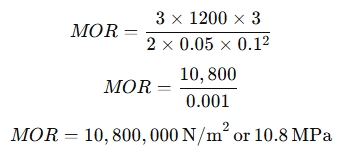
Modulus of Rupture for Concrete:
For concrete, the MOR is typically calculated using the flexural strength obtained from standardized tests like the four-point bending test.
Additional Notes:
- Units: Ensure your units are consistent. For example, if you are using meters for length, use Newtons for force, and your MOR will be in N/m² (Pa) or MPa. For inches and pounds, you’ll get psi.
- Materials: The Modulus of Rupture varies significantly depending on the material. For concrete, for example, it is usually lower than steel, which has a much higher MOR.