Calculate Pipe Friction Loss
To calculate the friction loss in a pipe, the Darcy-Weisbach equation is commonly used. This equation helps determine the energy loss (head loss) due to friction as the fluid moves through the pipe. The equation is as follows:
Darcy-Weisbach Equation:
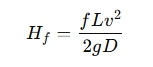
Where:
- Hf = Friction head loss (meters or feet)
- f = Friction factor (dimensionless)
- L = Length of the pipe (meters or feet)
- v = Velocity of the fluid (meters per second or feet per second)
- g = Acceleration due to gravity (9.81 m/s²)
- D = Diameter of the pipe (meters or feet)
Friction Factor f:
The friction factor depends on the flow regime (laminar or turbulent) and the roughness of the pipe. For laminar flow, the friction factor is given by:
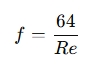
Where:
- Re = Reynolds number, which characterizes the flow regime and is calculated as:
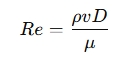
Where:
- ρ = Density of the fluid (kg/m³)
- v = Velocity of the fluid (m/s)
- D = Diameter of the pipe (m)
- μ = Dynamic viscosity of the fluid (Pa·s)
For turbulent flow, the friction factor is often found using empirical formulas, such as the Colebrook-White equation or approximated using charts.
Example Calculation:
Let’s say we have the following information:
- Pipe length L = 100 meters
- Pipe diameter D = 0.2 meters
- Fluid velocity v = 2 m/s
- Friction factor f = 0.02 (assuming turbulent flow)
- Acceleration due to gravity g = 9.81 m/s²
Step 1: Plug the values into the Darcy-Weisbach equation:
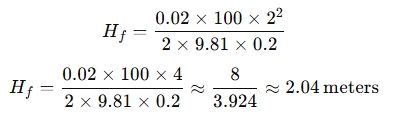
So, the friction head loss Hf is approximately 2.04 meters.