Pipe Line Velocity Calculator
To calculate the velocity of fluid in a pipeline, we use the continuity equation or the Darcy-Weisbach equation. The velocity of a fluid depends on the flow rate and the cross-sectional area of the pipe.
Formula for Pipe Line Velocity:
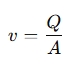
Where:
- v = Velocity of the fluid (m/s or ft/s)
- Q = Volumetric flow rate (m³/s or GPM)
- A = Cross-sectional area of the pipe (m² or ft²)
1. Volumetric Flow Rate (Q):
The flow rate is the volume of fluid passing a point in the pipe per unit time. It’s often given in units of cubic meters per second (m³/s) or gallons per minute (GPM).
2. Cross-sectional Area (A):
The cross-sectional area of a pipe is determined by its diameter. If the pipe is circular, the area is calculated as:
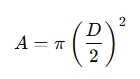
Where:
- D = Diameter of the pipe (meters or feet)
- π = 3.14159
Example Calculation:
Let's assume you have the following information:
- Flow rate (Q) = 10 L/s (liters per second)
- Pipe diameter (D) = 0.5 m
Step 1: Convert the flow rate into cubic meters per second (since 1 L = 0.001 m³):
Q=10 L/s=0.01 m³/sStep 2: Calculate the cross-sectional area of the pipe:
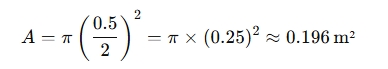
Step 3: Calculate the velocity:
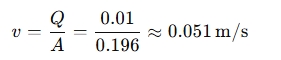
So, the velocity of the fluid in the pipeline is approximately 0.051 m/s.