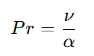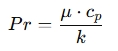The Prandtl number (Pr) is a dimensionless quantity used in fluid mechanics and heat transfer to compare the relative thickness of the velocity and thermal boundary layers. It is given by the formula:
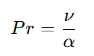
Where:
- ν is the kinematic viscosity (in m2/s),
- α is the thermal diffusivity (in m2/s).
Alternatively, the Prandtl number can be expressed as:
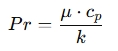
Where:
- μ is the dynamic viscosity (in Pa⋅s or kg/(m⋅s)),
- cp is the specific heat capacity (in J/(kg⋅K)),
- k is the thermal conductivity (in W/(m⋅K)).
Prandtl number values:
- Low Prandtl number (Pr < 1): Thermal diffusivity is higher than momentum diffusivity. This is typical for liquids like liquid metals.
- High Prandtl number (Pr > 1): Momentum diffusivity dominates over thermal diffusivity. This is common for oils, glycerin, and most gases.
- Prandtl number around 1: The diffusion of momentum and heat are comparable. This is typical for air and water.