Pressure Loading of Thin-walled Vessels (Sphere) Calculator
To calculate the pressure loading on a thin-walled spherical vessel, you can use the following formula:
For a thin-walled sphere under internal pressure:
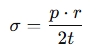
Where:
- = Hoop stress (or tensile stress) in the wall of the sphere (in Pascals, Pa)
- = Internal pressure (in Pascals, Pa)
- = Radius of the sphere (in meters, m)
- = Thickness of the wall (in meters, m)
For external pressure, the formula would depend on the material and the design. But for internal pressure, the above formula is typical for thin-walled vessels (where the wall thickness is much smaller than the radius ).
Additionally, the maximum internal pressure that a spherical vessel can withstand before yielding is given by:
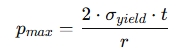
Where:
- σyield = Yield strength of the material (in Pascals, Pa)
This equation can help you determine the maximum pressure that the vessel can safely handle before the material yields.