Enter value and click on calculate. Result will be displayed.

Push - Pull for a Hydraulic Cylinder at Specified Angle
To calculate the force and motion in a hydraulic cylinder with a specified angle (often called a "push-pull" or "tilt angle" configuration), we need to consider the following:
- Cylinder Specifications: These include bore diameter (area), rod diameter (for calculating the effective area), and stroke length.
- Hydraulic Pressure: The pressure supplied to the hydraulic cylinder.
- Angle of Application: The angle at which the cylinder is acting, which affects the distribution of force along the axis of the cylinder.
- Load on Cylinder: The force required to be applied by the cylinder.
Here’s how the force can be calculated:
1. Calculate the Cross-sectional Area
-
Bore Area (A_bore): The area of the piston side is given by the formula:
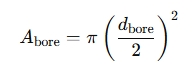
where dbored is the bore diameter.
-
Rod Area (A_rod): The area on the rod side of the cylinder is given by:
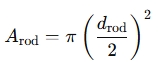
where drod is the diameter of the rod.
2. Calculate the Force
For a push force (with the piston extending):
- Force on Piston Side (F_push):
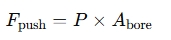
where is the hydraulic pressure.
For a pull force (with the rod side extending):
- Force on Rod Side (F_pull):
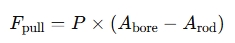
3. Adjust for the Angle
If the cylinder is operating at an angle (e.g., tilted), the effective force along the axis of the cylinder can be calculated by multiplying by the cosine of the angle ():
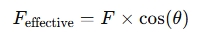
Where:
- is the force calculated above (either push or pull).
- is the angle between the force direction and the axis of the cylinder.
4. Consider the Load
The load applied on the cylinder will also depend on the angle. If the load is parallel to the cylinder’s axis, it will remain unchanged, but if the load is perpendicular or at an angle, you'll need to adjust the load force accordingly.