➔ Calculate Thermal Conductivity
➔ Calculate Thermal Resistance
➔ Calculate Thermal Conductance
➔ Calculate Specific Heat
Thermal Calculators
Here’s a breakdown of how to calculate each of the thermal properties you mentioned:
1. Thermal Conductivity (k)
Thermal conductivity refers to the ability of a material to conduct heat. It is a material property and depends on the type of material, temperature, and other factors.
The formula for thermal conductivity is:
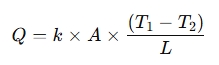
Where:
- Q = Heat transfer rate (W)
- k = Thermal conductivity (W/m·K)
- A = Area of the material (m²)
- T1 and T2 = Temperature difference between the two sides of the material (K or °C)
- L = Thickness of the material (m)
To solve for k, rearrange the equation:
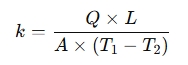
2. Thermal Resistance (R)
Thermal resistance is a measure of the ability of a material or system to resist the flow of heat. It's typically used when considering heat transfer across walls, windows, or insulation.
The formula for thermal resistance is:
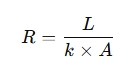
Where:
- R = Thermal resistance (K/W)
- L = Thickness of the material (m)
- k = Thermal conductivity of the material (W/m·K)
- A = Cross-sectional area (m²)
3. Thermal Conductance (C)
Thermal conductance is the inverse of thermal resistance and represents the ability of a material to conduct heat.
The formula for thermal conductance is:
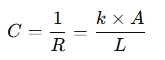
Where:
- C = Thermal conductance (W/K)
- k = Thermal conductivity (W/m·K)
- A = Area of the material (m²)
- L = Thickness of the material (m)
4. Specific Heat (Cp)
Specific heat is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of a given mass of a material by one degree Celsius (or one Kelvin).
The formula for specific heat is:

Where:
- Q = Heat energy absorbed or released (J)
- m = Mass of the substance (kg)
- Cp = Specific heat capacity (J/kg·K)
- ΔT = Change in temperature (K or °C)
To solve for Cp:
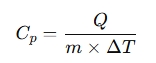
Example Calculations:
Let’s go through an example for each property:
1. Thermal Conductivity Calculation:
Given:
- Heat transfer rate Q = 100 W
- Area A = 2 m²
- Temperature difference (T1−T2) = 10°C (or 10 K)
- Thickness L = 0.5 m
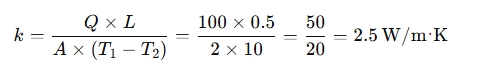
So, the thermal conductivity is 2.5 W/m·K.
2. Thermal Resistance Calculation:
Given:
- L = 0.5 m
- k = 2.5 W/m·K
- A = 2 m²
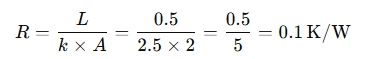
So, the thermal resistance is 0.1 K/W.
3. Thermal Conductance Calculation:
Given:
- k = 2.5 W/m·K
- A = 2 m²
- L = 0.5 m
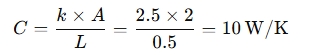
So, the thermal conductance is 10 W/K.
4. Specific Heat Calculation:
Given:
- Heat energy Q = 500 J
- Mass m = 2 kg
- Temperature change ΔT = 10°C
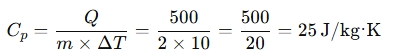
So, the specific heat is 25 J/kg·K.