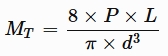
MT = Transverse Strength
P = Breaking Load
L = Distance Between Knife Edges on which the Sample is Supported
d = Average Specimen Diameter
Transverse Strength Calculator
The Transverse Strength (also known as Modulus of Rupture in certain contexts) is a material property that quantifies the ability of a material (typically a beam or a structural element) to resist failure under bending. It is particularly important for materials subjected to bending loads, such as beams, plates, and other structural elements.
Transverse Strength (Modulus of Rupture) Formula:
For a beam subjected to a bending load, the transverse strength can be calculated using the following formula:
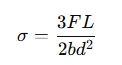
Where:
- σ = Transverse Strength (Modulus of Rupture) in units of stress (Pa or psi)
- F = Maximum load applied to the beam (N or lb)
- L = Length of the span of the beam (m or ft)
- b = Width of the beam (m or ft)
- d = Depth (height) of the beam (m or ft)
Explanation of Parameters:
- F: This is the maximum force applied to the beam at the midpoint (for a simply supported beam under uniform loading).
- L: The distance between the two supports of the beam.
- b: The width of the beam.
- d: The depth or height of the beam.
This formula assumes a simply supported beam with a point load applied at the center.
Units:
- N (Newton) for force, or lb (pound-force).
- m (meter) for length, or ft (foot).
- Pa (Pascal) or MPa (Megapascal) for stress. If you're using psi for stress, make sure you convert all units accordingly.
Example Calculation:
Let’s say you have a wooden beam with the following parameters:
- Maximum load (F) = 1,500 N
- Span length (L) = 3 m
- Width (b) = 0.05 m
- Depth (d) = 0.1 m
Using the formula:
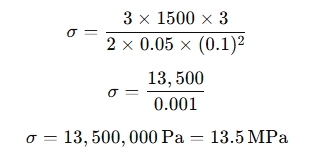
The transverse strength (or modulus of rupture) is 13.5 MPa
Applications of Transverse Strength:
- Construction and Structural Engineering: To ensure that beams, slabs, and other structural elements will withstand bending forces.
- Material Testing: Used in laboratories to test the bending strength of materials like wood, concrete, plastics, and metals.
- Woodworking and Construction: Ensuring that timber beams and planks used in construction can handle the expected loads without failing.