Turbulent Pipe Flow Calculator
To calculate turbulent pipe flow, we can use the Darcy-Weisbach equation for head loss in pipes:
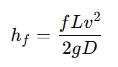
Where:
- is the head loss (meters or feet)
- is the Darcy friction factor (dimensionless)
- is the length of the pipe (meters or feet)
- is the velocity of the fluid (meters per second or feet per second)
- is the acceleration due to gravity (9.81 m/s² or 32.2 ft/s²)
- is the diameter of the pipe (meters or feet)
Friction Factor Calculation
For turbulent flow, the friction factor f can be calculated using the Colebrook-White equation, which is implicit:
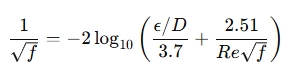
Where:
- is the roughness of the pipe (meters or feet)
- is the diameter of the pipe (meters or feet)
- is the Reynolds number (dimensionless)
Reynolds Number Calculation
The Reynolds number ReRe is calculated using the following formula:
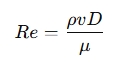
Where:
- is the density of the fluid (kg/m³ or lb/ft³)
- is the velocity of the fluid (m/s or ft/s)
- is the diameter of the pipe (m or ft)
- is the dynamic viscosity of the fluid (kg/(m·s) or lb/(ft·s))