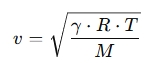The velocity of sound refers to the speed at which sound waves propagate through a medium. It is affected by factors such as the medium's properties (e.g., density, temperature) and can vary depending on whether the medium is a solid, liquid, or gas.
General Formula for the Velocity of Sound:
For air at standard conditions (at sea level, 20°C or 68°F), the speed of sound is approximately 343 m/s (meters per second).
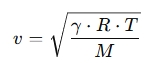
Where:
- v = speed of sound (m/s)
- γ = adiabatic index (ratio of specific heats) of the gas (for air, γ ≈ 1.4)
- R = universal gas constant (8.314 J/(mol·K))
- T = temperature in Kelvin (K)
- M = molar mass of the gas (for air, M ≈ 0.029 kg/mol)
Key Factors Affecting the Velocity of Sound:
-
Temperature:
- The speed of sound increases with an increase in temperature. This is because the molecules in the air (or any other medium) move faster at higher temperatures, allowing sound waves to propagate more quickly.
- A general approximation for air is:
vair≈331.3+0.6*T
Where v is the speed of sound in m/s, and T is the temperature in Celsius.
-
Medium (Air, Water, Solids):
- The speed of sound is faster in denser mediums like solids than in gases. For instance:
- In air (at 20°C): 343 m/s
- In water: Around 1,480 m/s
- In steel: Around 5,960 m/s
-
Humidity:
- In moist air (higher humidity), sound travels faster than in dry air because the density of air decreases with the addition of water vapor, making it less dense.
-
Pressure:
- For gases, under normal conditions, pressure does not significantly affect the velocity of sound, as long as temperature is constant. However, for liquids and solids, higher pressure can increase sound speed due to greater molecular interactions.
Examples of Sound Velocity in Different Mediums:
- Air (at 20°C): 343 m/s
- Water (at 20°C): 1,480 m/s
- Steel: 5,960 m/s
- Helium (at 0°C): 1,000 m/s
Sound Speed at Different Temperatures:
For air, the speed of sound increases with temperature:
- At 0°C, the speed of sound is around 331 m/s.
- At 20°C, the speed of sound is 343 m/s.
- At 100°C, the speed of sound is 386 m/s.
Quick Calculation:
If you want to approximate the speed of sound at a certain temperature in air, you can use this simplified formula:
Vair=331.3+(0.6×T)
Where T is the temperature in Celsius.
Example:
At 25°C:
Vair=331.3+(0.6×25)=346.3 m/s