Transistor Switch Saturation Calculator
What is a Transistor Switch Saturation Calculator?
A Transistor Switch Saturation Calculator is a tool used to determine the required base current (Ib) to fully turn on a BJT (Bipolar Junction Transistor) in saturation mode when used as a switch. In saturation mode, the transistor acts as a closed switch, allowing maximum current flow from collector to emitter with minimal voltage drop.
The key formula is:
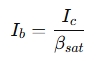
where:
- Ib = Base current (A)
- Ic = Collector current (A)
- β_sat = Saturation gain (usually 5 to 20, much lower than the transistor’s nominal β)
Why Use a Transistor Switch Saturation Calculator?
Manually determining the right base resistor (Rb) and Ib can be tricky. This calculator helps:
- Ensure reliable switching in microcontroller and digital circuits.
- Avoid underdriving the transistor, which may cause slow or incomplete switching.
- Prevent excessive base current, reducing power loss.
- Save time in circuit design and troubleshooting.
How to Use a Transistor Switch Saturation Calculator?
- Enter the collector current (Ic) needed for your load.
- Enter the transistor’s saturation β (β_sat) (commonly 5–20).
- Enter the input voltage (V_in) (e.g., microcontroller output voltage).
- Enter the base-emitter voltage (Vbe) (typically 0.7V for silicon BJTs).
- The calculator will compute:
- Base current (Ib) required for saturation.
- Base resistor (Rb) using:
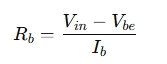
- Use the resistor value to drive the transistor properly in switching applications.
When to Use a Transistor Switch Saturation Calculator?
- When designing relay drivers, LED controllers, or motor switches.
- In microcontroller-based circuits (Arduino, PIC, Raspberry Pi, etc.).
- When ensuring fast and efficient transistor switching.
- While troubleshooting slow or incomplete transistor switching in circuits.