Butterworth Pi LC Low Pass Filter Calculator
A Butterworth Pi LC Low-Pass Filter Calculator is a tool used to design a Butterworth low-pass filter in a π (pi) configuration using inductors (L) and capacitors (C). This type of filter is designed for maximally flat frequency response, which means it has no ripple in the passband and a smooth, predictable roll-off beyond the cutoff frequency.
Structure of a Pi LC Low-Pass Filter:
The "π" shape comes from the arrangement of components:
Two capacitors (C1, C2) in parallel (to ground).
One inductor (L) in series between the capacitors.
Visually, it looks like the Greek letter "π".
How it works:
Low frequencies: Easily pass through the inductor and avoid the capacitors, reaching the output.
High frequencies: Are shunted to ground by the capacitors and face impedance from the inductor, reducing their amplitude.
What the calculator does:
It helps you determine the right L and C values based on your design specs:
Cutoff frequency (Fc): The frequency where attenuation begins.
Load impedance (Z): The impedance of the connected load.
Filter order: The number of LC sections, affecting steepness of attenuation.
For a second-order (2-pole) Butterworth low-pass filter, the values are calculated for:
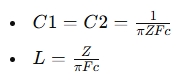
Why choose a Butterworth Pi low-pass filter?
Pros:
Smooth, flat response with no passband ripple.
Good balance of simplicity and performance.
Cons:
Slower roll-off compared to Chebyshev or elliptic filters.