Resistor voltage division calculation
What is Resistor Voltage Division?
Resistor voltage division is a principle used to calculate the voltage drop across individual resistors in a series circuit. According to this principle, the voltage across each resistor in a series circuit is proportional to its resistance value.
The Resistor Voltage Division Calculator helps calculate the voltage across each resistor when multiple resistors are connected in series, given the total supply voltage.
Why is it Important?
Understanding and calculating voltage division is crucial in:
- Power distribution: Knowing how the supply voltage is shared across components helps you design circuits and protect components from excessive voltage.
- Signal processing: In many signal conditioning circuits, you need to ensure that each part of the circuit receives the correct voltage.
- Voltage regulation: Ensuring the proper voltage drop across components can be important in regulating voltage in specific parts of a circuit.
How Does it Work?
The voltage division rule states that the voltage drop across a resistor in a series circuit is proportional to its resistance.
The formula for the voltage drop across a resistor RiR_i R i in a series circuit is:
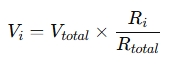
Where:
- Vi is the voltage across resistor RiR_i R i ,
- Vtotal is the total supply voltage,
- Ri is the resistance of the resistor ii i,
- Rtotal is the total resistance of the series circuit (sum of all resistances: Rtotal=R1+R2+⋯+Rn ).
Why Use a Calculator?
The Resistor Voltage Division Calculator allows you to quickly find the voltage across each resistor in a series circuit without having to manually apply the formula to each one. It can be particularly useful when dealing with circuits with many resistors, as it automates the calculation and minimizes the chance for errors.
When Do You Use Resistor Voltage Division?
You use voltage division in the following situations:
- When you have resistors connected in series: This is the primary case where voltage division is applicable.
- In voltage divider circuits: These are circuits where you intentionally divide a voltage between two or more resistors (e.g., for creating reference voltages, biasing, etc.).
- When designing circuits: In many designs, especially analog circuits, understanding the voltage distribution across resistors helps ensure the correct operation of each component.
Example:
Let's say you have a series circuit with three resistors: R1=2 Ω, R2=3 Ω, and R3=5 Ω, connected to a 12V power supply. The total resistance is:
Rtotal=R1+R2+R3=2+3+5=10 ΩThe voltage drop across R1R_1 R 1 would be:
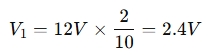
Similarly, you can calculate the voltage drop across R2 and R3 .
When Do You Need to Calculate Resistor Voltage Division?
You'd use this calculation whenever you need to:
- Determine how much voltage will be applied to specific components in a series circuit.
- Design voltage divider circuits for controlling or measuring voltages.
- Ensure components receive the correct voltage in a circuit.