Op Amp High Pass Filter Calculator
An Op Amp High Pass Filter Calculator is a tool used to calculate the characteristics of a high-pass filter circuit built using an operational amplifier (op-amp). A high-pass filter allows high-frequency signals to pass through while attenuating lower-frequency signals, which is the opposite of a low-pass filter.
What is an Op Amp High Pass Filter?
An Op Amp High Pass Filter is an electronic filter that allows high-frequency signals to pass through, while attenuating (reducing the amplitude of) signals that are lower in frequency. It uses an operational amplifier, resistors, and capacitors to achieve this frequency-dependent behavior.
- High-pass filters are used to remove low-frequency noise or unwanted components of a signal, allowing only the higher frequencies to pass.
- It’s useful in situations where you want to isolate higher-frequency components of a signal (for example, in audio systems to filter out low-frequency noise or hum).
Why Use an Op Amp High Pass Filter?
- Noise reduction: High-pass filters can be used to remove unwanted low-frequency noise, such as power line hum (50/60 Hz) or drift, from signals in communication and audio systems.
- Signal conditioning: They are used in systems where only higher-frequency components are of interest, and low-frequency components are either noise or irrelevant (e.g., in signal processing or audio equalization).
- Separation of frequencies: In applications where you want to isolate certain frequencies (such as in a speaker crossover, where high-pass filters allow high frequencies to pass to tweeters and block lower frequencies).
- Prevention of distortion: By filtering out low-frequency components that may cause distortion, the signal remains cleaner and more accurate.
How Does an Op Amp High Pass Filter Work?
An op-amp high-pass filter works by using a combination of capacitors and resistors to create a frequency-dependent behavior. It allows high frequencies to pass through the circuit while attenuating lower frequencies.
The basic components of an op-amp high-pass filter:
- Resistor (R): The resistor determines the impedance and time constant of the filter.
- Capacitor (C): The capacitor works with the resistor to set the cutoff frequency, beyond which the filter allows signals to pass.
- Op-Amp: The operational amplifier amplifies the signal to the desired level and allows the circuit to function as a filter.
High-Pass Filter Behavior:
- At low frequencies: The impedance of the capacitor is high, and most of the signal is blocked or attenuated by the capacitor.
- At high frequencies: The impedance of the capacitor becomes very low, allowing most of the signal to pass through the circuit.
The cutoff frequency (fc ) is the frequency at which the filter starts to significantly attenuate the signal. Below the cutoff frequency, the signal is increasingly attenuated.
Op Amp High Pass Filter Calculation:
The key parameter in a high-pass filter is the cutoff frequency fc , which determines the point at which the signal begins to attenuate. The cutoff frequency is calculated using the formula:
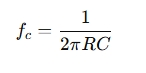
Where:
- fc = cutoff frequency (in Hz)
- R= resistance (in ohms, Ω)
- C = capacitance (in farads, F)
This formula calculates the cutoff frequency at which the output power drops to half (or -3 dB) of its maximum value.
Example:
Let’s say you want to design a high-pass filter with a cutoff frequency of 500 Hz and you are using a resistor of 10 kΩ. To find the necessary capacitor value:
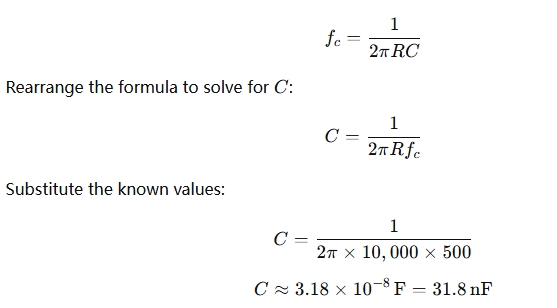
So, to create a high-pass filter with a cutoff of 500 Hz, you would need a 31.8 nF capacitor in combination with the 10 kΩ resistor.
When Should You Use an Op Amp High Pass Filter Calculator?
- When designing filters: If you need to design a high-pass filter for a specific application, you can use the calculator to select the correct resistor and capacitor values based on your desired cutoff frequency.
- Noise filtering: In systems where low-frequency noise (like hum) needs to be filtered out of a signal (e.g., in audio systems), a high-pass filter helps remove unwanted low frequencies.
- Signal conditioning: In applications where you need to isolate or emphasize higher-frequency components, such as in equalizers, audio amplifiers, or communication systems.
- Frequency separation: If you are working with systems that require separating signals by frequency, such as in speaker crossovers where you want to send only the high frequencies to tweeters, a high-pass filter is essential.
Types of High Pass Filters:
- First-order high-pass filter: The simplest type, typically implemented with a single resistor and capacitor, which attenuates the signal at a rate of 20 dB per decade after the cutoff frequency.
- Second-order or higher filters: These involve more complex configurations and provide steeper attenuation slopes, useful for applications requiring more precise frequency control.
Practical Applications:
- Audio systems: High-pass filters are commonly used in audio equipment to filter out low-frequency noise, such as hum from power lines, or to isolate the high-frequency components of an audio signal.
- Communication systems: High-pass filters help remove unwanted low-frequency interference from communication signals, improving signal clarity.
- Speaker systems: In speaker crossover networks, high-pass filters are used to direct only the higher frequencies to the tweeters while blocking lower frequencies to avoid damage and distortion.
- Signal processing: High-pass filters are used in signal processing to remove low-frequency components from signals before further analysis or amplification.
- Power supply filtering: In power supplies, high-pass filters can be used to block low-frequency noise and ripple in the output signal.