Line Of Sight Calculator
What is a Line of Sight (LOS) Calculator?
A Line of Sight (LOS) Calculator is a tool used to determine whether two locations are directly visible to each other, taking into account the curvature of the Earth and potential obstacles (like buildings, mountains, etc.). It's typically used in radio communication, wireless networking, satellite communications, and surveying.
Why Use It?
Communication Reliability: Ensures that there are no obstacles between two points, guaranteeing that signals (RF, optical, etc.) can travel freely without interference.
Network Planning: Helps in placing antennas, radios, or satellites to ensure optimal coverage.
Safety and Regulations: Helps avoid situations where infrastructure (like towers) could block signals, and ensures compliance with regulations for line-of-sight transmission.
Signal Strength: Predicts the potential strength of signals, especially in long-distance communication or wireless links.
How Does It Work?
The LOS calculation considers:
Earth's curvature: Since the Earth is round, the higher the transmission point, the farther the visible distance.
Antenna height: The height of both the transmitter and the receiver impacts visibility.
Obstacles: Hills, mountains, buildings, and other structures can obstruct the line of sight.
For basic LOS calculation between two points:
The line of sight distance (in kilometers) can be approximated using:
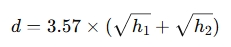
Where:
d = distance between two points (in kilometers)
h1 and h2 = heights of the two antennas (in meters)
If the LOS is blocked by obstacles, you'll need to adjust for them using obstacle heights and the relative terrain elevation.
When to Use It?
Radio frequency planning: Ensuring wireless communication between stations or repeaters is possible without interference.
Satellite links: Verifying that satellites can "see" ground stations.
Long-distance Wi-Fi links: Ensuring no obstacles will block the signal.
Surveying: Determining if one location can visually "see" another, useful in real estate, construction, and geospatial applications.
Antenna installations: Ensuring proper placement for optimal signal coverage.