R-C Filter Cutoff Frequency Calculator
What is an R-C Filter Cutoff Frequency Calculator?
An R-C Filter Cutoff Frequency Calculator is a tool used to calculate the cutoff frequency of an R-C (Resistor-Capacitor) filter. An R-C filter is a basic circuit used to filter signals based on their frequency. It consists of a resistor (R) and a capacitor (C) arranged in either a low-pass or high-pass configuration. The cutoff frequency is the frequency at which the filter begins to significantly attenuate the signal.
Why Use an R-C Filter Cutoff Frequency Calculator?
- Designing Filters: If you're designing an R-C filter circuit and need to select the appropriate resistor and capacitor values to achieve a specific cutoff frequency, this calculator helps simplify the process.
- Signal Processing: In many applications, you need to isolate or remove certain frequency ranges from a signal. This calculator helps determine the cutoff point at which the filter will start to attenuate unwanted frequencies.
- Noise Reduction: When you want to remove high-frequency noise from a signal (or vice versa), calculating the correct cutoff frequency ensures the filter effectively filters out the noise.
- Frequency Selection: It helps select the right frequency for the system, ensuring that only desired frequencies pass through and others are blocked.
How Does an R-C Filter Work?
An R-C filter is a simple passive electronic circuit made of a resistor (R) and a capacitor (C). Depending on the configuration (low-pass or high-pass), the filter allows certain frequencies to pass through while attenuating others:
- Low-pass filter: Allows low-frequency signals to pass and attenuates high-frequency signals.
- High-pass filter: Allows high-frequency signals to pass and attenuates low-frequency signals.
The cutoff frequency (fc ) is the frequency at which the output signal is reduced to approximately 70.7% (or -3 dB) of its maximum value. Below the cutoff frequency, the signal is passed with little attenuation, and above the cutoff, the signal is attenuated more.
R-C Filter Cutoff Frequency Calculation
For both low-pass and high-pass filters, the cutoff frequency is calculated using the same formula:
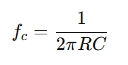
Where:
- fc = cutoff frequency in Hertz (Hz)
- R= resistance in ohms (Ω)
- C = capacitance in farads (F)
Steps to Calculate the Cutoff Frequency:
- Determine the Resistor (R): Choose the appropriate resistor value based on your design.
- Determine the Capacitor (C): Choose the capacitor value based on the desired filter characteristics.
- Apply the Formula: Plug the values of RR R and CC C into the formula to find the cutoff frequency.
Example 1: Low-Pass Filter Calculation
Suppose you have a low-pass filter with a 10 kΩ resistor and a 100 nF capacitor.
Using the formula:
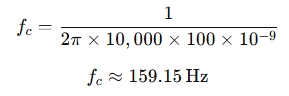
So, the cutoff frequency is approximately 159.15 Hz.
Example 2: High-Pass Filter Calculation
Suppose you have a high-pass filter with a 100 kΩ resistor and a 10 nF capacitor.
Using the formula:
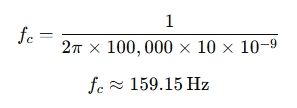
Again, the cutoff frequency is approximately 159.15 Hz.
When Should You Use an R-C Filter Cutoff Frequency Calculator?
You should use the R-C filter cutoff frequency calculator when:
- Designing Filters: You need to design an R-C low-pass or high-pass filter for a specific application, such as noise reduction, signal conditioning, or frequency separation.
- Signal Processing: If you're working with signals that require specific frequency bands to be passed through (e.g., in audio or sensor systems), you will need to calculate the appropriate cutoff frequency for the filter.
- Frequency Range Selection: When you want to isolate or filter out certain frequency ranges from a signal, such as removing low-frequency hum or high-frequency noise.
- Circuit Design: When you're building a circuit that requires frequency-specific filtering (e.g., in audio amplifiers, communication systems, or power supplies).
- Troubleshooting: If you need to modify an existing circuit or filter to meet specific frequency requirements, the calculator helps determine the correct cutoff frequency.
Practical Applications of R-C Filters:
- Audio Systems: R-C filters are commonly used in audio systems to filter out unwanted frequencies, such as using a low-pass filter to remove high-frequency noise or using a high-pass filter to block low-frequency hum.
- Signal Processing: In signal processing, R-C filters are used to shape the frequency response of circuits, removing undesired frequencies while allowing others to pass.
- Communication Systems: Filters are essential for communication systems (such as radio, television, or cellular networks) to isolate specific frequency bands for transmission or reception.
- Power Supplies: R-C filters can smooth out signals and reduce noise in power supply circuits, ensuring stable voltage.
- Sensor Systems: In sensor applications, R-C filters are used to filter out noise or unwanted signal components before further analysis.