Skin Effect Calculator
A Skin Effect Calculator is a tool used to calculate the skin effect in conductors carrying alternating current (AC). The skin effect refers to the tendency of AC to flow mainly near the surface of a conductor, rather than uniformly throughout its cross-sectional area. This effect increases with the frequency of the AC, leading to higher resistance at higher frequencies.
The Skin Effect Calculator typically helps in determining the following:
Skin Depth (δ): The distance from the surface of the conductor where the current density has dropped to 1/e (about 37%) of its value at the surface. It depends on the frequency of the AC, the material's conductivity, and the permeability of the material.
The formula for skin depth is:
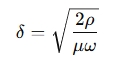
Where:
δ = Skin depth (meters)
ρ = Resistivity of the material (ohm-meter)
μ = Permeability of the material (Henries per meter)
ω = Angular frequency of the current (ω=2πf, where
f is the frequency in Hz)
Effect on Resistance: At higher frequencies, the effective resistance of the conductor increases because less current flows through the inner part of the conductor. The skin effect causes a concentration of current at the surface, which makes the conductor appear "smaller" in terms of effective cross-sectional area.
Impact on Signal Transmission: For high-frequency applications (like RF or microwave circuits), the skin effect can increase signal loss due to the increased resistance at the surface, affecting the efficiency of the transmission.
Why use a Skin Effect Calculator?
Designing high-frequency circuits: Helps design conductors that minimize power loss due to skin effect.
Cable and wire design: Important for high-speed data transmission and RF cables.
Signal integrity: Ensures that signal degradation is minimized in circuits like antennas and high-frequency transmission lines.