Sum calculator (sum of squares, sum of cubes, etc.)
A Sum Calculator for things like the sum of squares, sum of cubes, and other related operations is a tool used to compute specific mathematical sums quickly and easily. These kinds of sums are often used in various fields like statistics, physics, and engineering.
1. What is a Sum Calculator?
A sum calculator allows you to compute sums based on certain formulas. Some common types are:
- Sum of Squares: This is the sum of each number squared. For example, for the numbers 1, 2, and 3, the sum of squares would be
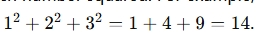 .
. - Sum of Cubes: This is the sum of each number cubed. Using the same numbers,
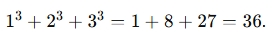 .
. - General Sums: You can calculate sums for a variety of sequences or powers, such as squares, cubes, or higher powers of numbers.
2. Why Use a Sum Calculator?
These calculators save time and effort in solving these specific sums, which are often needed for:
- Mathematical analysis (e.g., finding the sum of squared deviations in statistics).
- Physics and engineering (e.g., in calculating moments of inertia or other related properties).
- General use in formulas that require sums of squares or cubes, especially when dealing with large datasets.
3. How Does a Sum Calculator Work?
A sum calculator works by taking an input range of numbers and applying the respective formula. For example:
- Sum of Squares Formula:
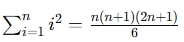 — it uses this formula to calculate the sum of squares of the first nn n numbers.
— it uses this formula to calculate the sum of squares of the first nn n numbers. - Sum of Cubes Formula:
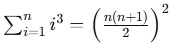 — similarly, the sum of cubes is calculated using a specific formula.
— similarly, the sum of cubes is calculated using a specific formula.
The calculator either uses a general formula for a range of numbers or can iterate through the range and apply the operation to each number.
4. When to Use a Sum Calculator?
You'd use this calculator when:
- You need to compute sums of squares or cubes for a given range of numbers. For example, when analyzing data or performing specific mathematical operations.
- In problem-solving that involves series or sequences of numbers where squares or cubes are involved.
- During exams or assignments that require quick calculations of these sums.