Formula:
M = ( x1+x2+x3 ) / 3 , ( y1+y2+y3 ) / 3
Centroid of a Triangle Calculator
What is a Centroid of a Triangle Calculator?
A Centroid of a Triangle Calculator computes the centroid (or center of mass) of a triangle. The centroid is the point where all three medians of a triangle intersect. It is often referred to as the "center of gravity" because it's the point at which the triangle would balance if it were made of a uniform material.
For a triangle with vertices at (x1,y1), (x2,y2), and (x3,y3), the coordinates of the centroid (xC,yC) are calculated as:
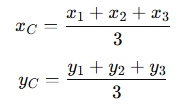
Why use a Centroid of a Triangle Calculator?
- Geometric Analysis: Helps quickly find the centroid, which is essential in geometry for solving problems related to balance, symmetry, and the center of mass.
- Engineering Applications: In structural design, the centroid is often used to find the center of mass for load distribution.
- Simplification: Quickly computes the centroid without manual calculations, especially useful for more complex triangles or when working with coordinates in design.
How does a Centroid of a Triangle Calculator work?
- Input: You provide the coordinates of the three vertices of the triangle.
- Process: The calculator calculates the average of the x-coordinates and y-coordinates of the three vertices to determine the centroid.
- Output: The result is the centroid's coordinates, (xC,yC).
For example, if the vertices of the triangle are (1,2), (4,6), and (7,3), the centroid would be:
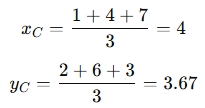
So, the centroid of the triangle is at (4,3.67).
When should you use a Centroid of a Triangle Calculator?
- Geometric Problems: When working on problems in geometry that require finding the centroid of a triangle.
- Engineering Design: When calculating the center of mass for a triangular component in mechanical or civil engineering.
- Physics: When analyzing forces or torque in systems with triangular shapes, especially in static equilibrium.
- Computer Graphics & Modeling: In 2D modeling or rendering, the centroid is used for transformations, object manipulation, or collision detection.