Formula:
v = 2πrT
Circular Velocity Calculator
A Circular Velocity Calculator is a tool used to calculate the velocity (speed) of an object moving in a circular path. This velocity is called "circular velocity" or "angular velocity", and it is crucial in physics and engineering to understand how fast an object moves along a curved trajectory.
Why use a Circular Velocity Calculator?
- Real-world applications: It’s used in many fields, such as astronomy (to calculate the velocity of planets or satellites), engineering (for designing rotating machinery), and sports (for analyzing the motion of objects in circular motion like a ball or a racing car).
- Convenience: It simplifies complex calculations, saving time and effort.
- Accurate results: It minimizes human error and gives precise values based on the inputs provided.
How does a Circular Velocity Calculator work?
The formula to calculate linear velocity (the velocity along the circular path) is:
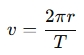
Where:
- v = circular (linear) velocity
- r = radius of the circle (distance from the center of the circle to the object)
- T = period of revolution (time taken for one complete revolution around the circle)
- π = constant (approximately 3.14159)
Alternatively, if the angular velocity ω\omega ω is known (in radians per second), you can calculate circular velocity as:
v = ω × rWhere:
- ω = angular velocity (rate at which the object moves through its circular path)
- r = radius
When to use a Circular Velocity Calculator:
- In physics: When analyzing objects in rotational motion (e.g., cars on curved tracks, satellites orbiting planets).
- In engineering: For rotating machinery like motors, gears, and turbines.
- In sports science: To study the motion of objects moving in curves, such as balls in games like soccer or tennis.
- In astronomy: To calculate the velocities of celestial bodies orbiting around other objects (like the Earth orbiting the Sun or satellites orbiting Earth).