Partial Pressure Calculator
What is a Partial Pressure Calculator?
A Partial Pressure Calculator determines the pressure exerted by an individual gas in a mixture, based on Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures. It helps analyze gas behavior in chemistry, physics, and engineering.
Why Use a Partial Pressure Calculator?
- To analyze gas mixtures (e.g., in chemistry, scuba diving, medical gases).
- To calculate oxygen levels in respiratory and aerospace applications.
- To predict reaction behavior in chemical equilibrium studies.
How to Calculate Partial Pressure?
Using Dalton’s Law:
Pi = Xi × PtotalWhere:
- Pi = Partial pressure of gas ii i
- Xi = Mole fraction of gas
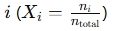
- Ptotal = Total pressure of the gas mixture
Steps:
- Find the mole fraction of the gas.
- Multiply by the total pressure to get partial pressure.
Alternatively, for ideal gases:
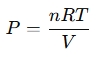
Where n = moles, R = gas constant, T = temperature, and V = volume.
When to Use It?
- In chemistry labs (e.g., gas reactions, equilibrium).
- In respiratory medicine (e.g., oxygen/nitrogen ratios in air).
- In scuba diving (e.g., gas mix calculations for safe breathing).
- In astronomy & aerospace (e.g., atmospheric pressure on planets).