Empirical Formula Calculator
What is an Empirical Formula Calculator?
An Empirical Formula Calculator is a tool that determines the simplest whole-number ratio of elements in a compound. It doesn’t show the exact number of atoms, just their relative proportions. For example, the empirical formula of glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) is CH₂O because it shows the simplest ratio of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
Why use an Empirical Formula Calculator?
- Saves time and reduces errors: Manual calculations can be tricky, especially for large compounds.
- Essential for chemistry studies: Understanding molecular composition starts with empirical formulas.
- Useful in research and industry: Helps identify unknown compounds from experimental data.
- Converts experimental data: When you have mass percentages or moles of elements, the calculator simplifies the process.
How does an Empirical Formula Calculator work?
- Input the mass or percentage of each element in a compound.
- Convert mass to moles using atomic masses from the periodic table:
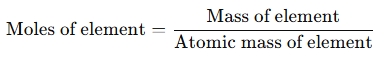
- Find the simplest whole-number ratio by dividing each element’s mole amount by the smallest number of moles.
- Get the empirical formula from the results.
Example:
For a compound with 40% carbon, 6.7% hydrogen, and 53.3% oxygen:
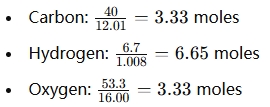
Divide all by 3.33:
- Carbon: 1
- Hydrogen: 2
- Oxygen: 1
Empirical formula: CH₂O
When to use an Empirical Formula Calculator?
- In lab work when analyzing experimental data.
- For chemical synthesis to ensure proper compound formulation.
- In academic studies when learning about chemical composition.
- For solving stoichiometry problems in chemical reactions.