Euler Number Calculator - Physics
The Euler number (often represented as "e") is a mathematical constant approximately equal to 2.71828. It plays a critical role in fields like physics, mathematics, and engineering, particularly in contexts involving growth, decay, and wave equations. The Euler number is commonly used when working with exponential functions, logarithms, and compound interest calculations, among other applications.
What is the Euler Number?
The Euler number (e) is the base of the natural logarithm. It arises naturally in many scenarios involving continuous growth or decay. For example, in population models or radioactive decay, quantities grow or shrink exponentially, and e is the base for those functions.
Why is it important?
In physics, the Euler number is important for describing systems where change is continuous. It's used in various equations, such as those modeling oscillations (like in mechanical vibrations or circuits), quantum mechanics, and thermodynamics.
How is it used?
Euler's number is used in many scientific formulas:
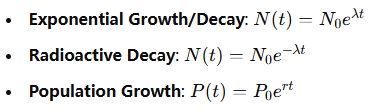
When is it used?
The Euler number appears whenever the rate of change of a quantity is proportional to the current value of that quantity. For example:
- When calculating interest in finance (compound interest),
- In physics for modeling radioactive decay or heat diffusion,
- In chemistry when studying reaction rates.
If you’re referring to an "Euler Number Calculator" in physics, it’s typically a tool that helps to calculate the results of exponential functions, growth, or decay models based on the Euler number. You input initial values, rates, and time intervals, and it computes the outcome.