Kilovolt-amps Calculation
What is kilovolt-amps (kVA)?
Kilovolt-amps (kVA) is a unit of apparent power in an electrical system. It represents the total power used by a device or system, including both the usable (real) power and the non-usable (reactive) power. Apparent power combines real power (measured in kilowatts, kW) and reactive power (measured in kilovolt-ampere reactive, kVAR).
Why is kVA important?
- Sizing electrical equipment: It helps in selecting transformers, generators, and UPS systems, ensuring they meet the power demand without overload.
- Power quality management: kVA includes both real and reactive power, giving a complete picture of the electrical load on a system.
- Avoiding power factor penalties: Utility companies may charge penalties when the power factor (real power ÷ apparent power) is too low.
How is kVA calculated?
The formula for kVA depends on the type of electrical system:
-
Single-phase system:
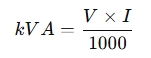
where:
- V = Voltage in volts
- I = Current in amperes
-
Three-phase system:
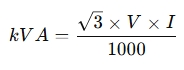
where:
- √3 = 1.732 (the square root of 3)
- VV V = Line-to-line voltage in volts
- II I = Current in amperes
When is kVA used?
- Designing electrical installations: Ensuring systems like HVAC, motors, and lighting get adequate power.
- Sizing backup systems: Choosing the right capacity for generators, inverters, and UPS units.
- Calculating load distribution: Balancing loads across different phases in a three-phase system.