Knudsen Number Calculator
A Knudsen Number Calculator is a tool used to determine the Knudsen number (Kn), which is a dimensionless quantity in fluid dynamics and gas dynamics. It describes the relative importance of molecular mean free path to a characteristic length scale of the system, helping to determine whether a gas behaves as a continuum or if rarefied gas effects become significant.
Why use a Knudsen Number Calculator?
The Knudsen number is crucial in:
- Aerospace engineering: For analyzing gas flows at high altitudes where the air is rarefied.
- Vacuum technology: To determine whether gases in vacuum systems behave as a continuum or as free molecular flow.
- Microfluidics & nanotechnology: Used in designing devices where gas flow occurs in very small channels.
- Heat transfer & semiconductor manufacturing: Helps in modeling gas interactions in extremely small spaces.
How does a Knudsen Number Calculator work?
The Knudsen Number (Kn) is defined as:
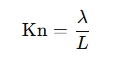
Where:
- λ is the mean free path of gas molecules (average distance a molecule travels before colliding with another molecule),
- L is a characteristic length scale of the system (such as pipe diameter or channel width).
The calculator computes Kn by taking the values of λ and L and performing the division.
When to use a Knudsen Number Calculator?
- Determining flow regimes: Used to classify the flow as:
- Continuum flow (Kn<0.01) → Normal fluid mechanics apply (Navier-Stokes equations valid).
- Slip flow (0.01≤Kn<0.1) → Slight deviation from classical fluid dynamics; slip conditions may apply.
- Transitional flow (0.1≤Kn<10) → Neither continuum nor free molecular assumptions hold well.
- Free molecular flow (Kn≥10) → Gas molecules move independently, requiring statistical mechanics for analysis.
- Designing vacuum systems: In ultra-high vacuum (UHV) systems, Knudsen number helps predict gas behavior.
- Aerospace & space exploration: Helps in studying rarefied gas dynamics for spacecraft moving through upper atmospheric layers.
- Microfluidics: Assists in determining gas flow properties in microscale devices like lab-on-a-chip systems.
Example Calculation
If a gas has:
- A mean free path λ = 0.1 mm,
- A characteristic length L = 10 mm,
Then,
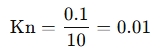
Since Kn=0.01, this indicates continuum flow with slip conditions.