Law of Cooling Calculator
A Law of Cooling Calculator is a tool designed to apply Newton’s Law of Cooling, which describes how an object’s temperature changes over time relative to the temperature of its surroundings.
What:
The Law of Cooling Calculator calculates how quickly an object cools down (or heats up) based on the difference between its temperature and the ambient temperature. It typically uses this formula:
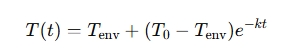
Where:
- T(t) = Temperature of the object at time tt t
- Tenv = Ambient (surrounding) temperature
- T0 = Initial temperature of the object
- k = Cooling constant (depends on the object’s material and environment)
- e = Euler’s number (approximately 2.718)
- t = Time elapsed
Why:
- Practical applications: It’s used in physics, engineering, and forensic science to estimate time of death, cooling rates of machines, and more.
- Predicting temperature changes: Helps determine how long an object takes to reach a stable temperature.
- Heat loss analysis: Useful in designing insulation and temperature control systems.
How:
- Input: You enter the initial temperature, surrounding temperature, cooling constant, and time.
- Calculation: It applies Newton’s Law of Cooling formula to find the temperature at a given time.
- Output: It shows the object’s temperature after the specified time.
When:
Newton’s Law of Cooling was formulated by Sir Isaac Newton in 1701, but calculators that apply this law — both physical and digital — became available much later. Modern versions are often found online as scientific tools or integrated into advanced calculators.