Molar Mass of Gas Calculator
A Molar Mass of Gas Calculator is a tool used to calculate the molar mass (or molecular weight) of a gas. The molar mass is the mass of one mole of gas molecules and is expressed in grams per mole (g/mol).
Why use a Molar Mass of Gas Calculator?
The molar mass of a gas is an important value in chemistry because it allows you to convert between the mass of a gas and the number of moles. Understanding the molar mass helps in determining the amount of substance present in a sample, and is essential for stoichiometric calculations, gas laws, and chemical reactions involving gases.
How does a Molar Mass of Gas Calculator work?
The molar mass of a gas can be calculated using the Ideal Gas Law or by knowing the composition of the gas:
-
Using the Ideal Gas Law: The Ideal Gas Law states that:
PV=nRTWhere:
- P is pressure,
- V is volume,
- n is the number of moles,
- R is the gas constant,
- T is temperature (in Kelvin).
Rearranging this equation to solve for molar mass (M):
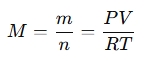
Where:
- m is the mass of the gas,
- n is the number of moles.
-
Using Composition: For a mixture or a compound gas, you can calculate the molar mass by summing the atomic masses of the elements present based on their molecular formula. For example, for CO2 , the molar mass would be the sum of the atomic masses of carbon (12.01 g/mol) and two oxygen atoms (2 × 16.00 g/mol).
The calculator will either use the ideal gas law or the molecular formula to compute the molar mass of the gas.
When to use a Molar Mass of Gas Calculator?
- Chemistry experiments: When you're dealing with gases and need to know the molar mass for conversions or chemical reactions.
- Stoichiometry: To determine how much of a gas is involved in a reaction, or how much of a substance you’ll need for a reaction involving gases.
- Gas law calculations: For determining the behavior of gases (like pressure, volume, or temperature) in relation to each other.
- Determining unknown gases: If you know the conditions (pressure, volume, and temperature) of a gas, you can calculate its molar mass and identify it.