Ohms Law Current Calculator
An Ohm's Law Current Calculator is a tool used to calculate the electric current (I) flowing through a conductor or component in a circuit based on the voltage (V) and resistance (R) of the circuit. It applies Ohm's Law, which is a fundamental principle in electrical engineering that describes the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance.
What is Ohm's Law?
Ohm's Law states that the current flowing through a conductor (such as a wire or resistor) is directly proportional to the voltage across it and inversely proportional to the resistance. The law is expressed with the formula:
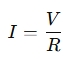
Where:
- I = Current (in amperes, A)
- V = Voltage (in volts, V)
- R = Resistance (in ohms, Ω)
This formula means that for a given voltage, if the resistance increases, the current decreases, and if the resistance decreases, the current increases.
Why use an Ohm's Law Current Calculator?
- Quick Calculations: It saves time by instantly calculating the current once you input the voltage and resistance.
- Accuracy: Ensures precise results for electrical circuits, minimizing the chance of mistakes when performing manual calculations.
- Convenient: It eliminates the need to memorize and apply the formula for every calculation, making it user-friendly.
- Widely Used: It’s a useful tool for anyone dealing with electrical circuits, from hobbyists to engineers, because it simplifies solving circuit problems.
How does an Ohm's Law Current Calculator work?
- Input:
- The Voltage (V) applied across the component or circuit.
- The Resistance (R) of the component or circuit.
- Calculation:
- The calculator applies the formula I=V/R to compute the current (I).
- Output:
- The result is the current (I) flowing through the circuit, measured in amperes (A).
When should you use an Ohm's Law Current Calculator?
- In electrical engineering and electronics:
- When designing or analyzing circuits and you need to calculate the current based on known voltage and resistance values.
- For troubleshooting circuits:
- If you're diagnosing electrical problems and need to calculate the current for different parts of a circuit to check if everything is working properly.
- In education:
- When learning about electrical principles, especially in physics and engineering courses where Ohm's Law is fundamental.
- For DIY projects:
- When working on projects involving electronics or electrical systems (e.g., building or repairing circuits, understanding power supplies).
- In industrial applications:
- To ensure proper electrical loads and prevent overloading by calculating the expected current in the circuit.