Formula:
change = ( V2 - V1 / |V1| ) x 100
Percentage Change Calculator
A Percentage Change Calculator is a tool used to calculate the percentage change between two values, showing how much something has increased or decreased relative to its original value. This is often used to track changes in prices, quantities, or other data points over time.
What is Percentage Change?
The percentage change expresses how much a value has increased or decreased relative to its initial value, and it is calculated using the following formula:
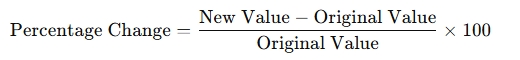
Where:
- New Value = The final or updated value
- Original Value = The initial value before the change
If the result is positive, it represents a percentage increase, and if the result is negative, it represents a percentage decrease.
Why use a Percentage Change Calculator?
- Saves Time: It quickly calculates percentage change without manually doing the math.
- Ensures Accuracy: Helps avoid errors in calculations, especially when the changes are small or large.
- Real-World Applications: Frequently used in business, economics, finance, and everyday calculations like sales or price changes.
- Easy to Understand: Provides a clear view of how much a value has changed in percentage terms, making it easy to analyze.
How does a Percentage Change Calculator work?
- Input:
- Original Value (the starting value)
- New Value (the updated value after the change)
- Calculation:
- The calculator subtracts the original value from the new value, divides that difference by the original value, and multiplies by 100 to convert it into a percentage.
- Output:
- The result is the percentage change, indicating the increase or decrease between the two values.
When should you use a Percentage Change Calculator?
- In business and finance:
- To track price changes, revenue growth, cost increases, or profit margins.
- To measure the change in the value of investments, such as stock prices or returns.
- For budgeting and cost analysis:
- Analyzing changes in expenses, income, or savings over a period.
- In retail or e-commerce:
- Calculating changes in product prices or discounts.
- In economics and statistics:
- Measuring inflation rates, population growth, or economic indicators.
- In education:
- Analyzing changes in student performance, such as grade improvements or test score differences.