Rectangular Weir Flow Rate Calculator
A Rectangular Weir Flow Rate Calculator is a tool used in fluid mechanics and hydrology to estimate the flow rate of water over a rectangular weir — a flat, rectangular-shaped notch typically placed across an open channel. It helps measure and control water flow in canals, rivers, and treatment systems.
Why use a Rectangular Weir Flow Rate Calculator?
- Flow Measurement: It provides a simple and effective way to measure the discharge of water from an open channel.
- Hydraulic Engineering: Engineers use it to design and manage irrigation systems, wastewater treatment plants, and stormwater drainage.
- Accuracy: It minimizes errors when calculating flow rates, especially when flow conditions vary.
- Monitoring and Control: Helps manage water distribution, flood control, and reservoir outflows.
How does a Rectangular Weir Flow Rate Calculator work?
The calculator typically uses this formula:
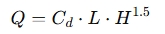
Where:
- Q = Flow rate (cubic meters per second or gallons per minute)
- Cd = Discharge coefficient (a value based on weir shape and conditions)
- L = Length of the weir opening (meters or feet)
- H = Height of the water above the weir crest (meters or feet)
Input:
- Weir length (L)
- Water height above the weir (H)
- Discharge coefficient (Cd ) — often between 0.6 and 0.65 for standard weirs
Calculation: The calculator applies the formula to determine the water’s flow rate.
Output: The flow rate is given in the desired unit, often with additional insights like flow regime (free-flowing or submerged).
When should you use a Rectangular Weir Flow Rate Calculator?
- In agriculture: To manage and monitor water flow in irrigation channels.
- For hydrology studies: To measure stream or river discharge in field research.
- In wastewater treatment: To control water levels and flow rates in settling tanks.
- For civil engineering: In designing dams, canals, and flood control systems.