Specific Gas Constant Calculator
A Specific Gas Constant Calculator is a tool used to calculate the specific gas constant (R) for a given gas. The specific gas constant is a fundamental constant in thermodynamics that is used to relate the pressure, volume, and temperature of a gas in equations such as the Ideal Gas Law.
Why Specific Gas Constant Calculator is used:
It is used because the specific gas constant is crucial for solving thermodynamic problems, particularly in understanding the behavior of gases. It allows engineers, scientists, and students to:
- Calculate thermodynamic properties of gases.
- Predict gas behavior under different conditions.
- Analyze efficiency in various processes like refrigeration, combustion, and air conditioning.
The specific gas constant R is unique to each gas and can be used to determine how a gas will behave under varying pressure and temperature.
How Specific Gas Constant Calculator works:
The specific gas constant is related to the universal gas constant Ru by the formula:
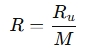
Where:
- R is the specific gas constant for the gas (in J/kg·K).
- Ru is the universal gas constant, which is approximately 8.314 J/mol·K.
- M is the molar mass of the gas (in kg/mol).
The calculator works by taking the molar mass of the gas and using the formula to calculate the specific gas constant for that particular gas.
When to use Specific Gas Constant Calculator:
You would use this calculator when:
- Performing thermodynamic calculations: When solving problems related to the behavior of gases, such as applying the Ideal Gas Law.
- Studying gases: To understand or analyze how different gases respond to changes in temperature and pressure.
- Engineering applications: In designing systems like engines, HVAC systems, or chemical reactors, where gas behavior needs to be accounted for.
- Research and experimentation: In laboratory work involving the properties of gases, such as when studying the performance of engines, compressors, or atmospheric studies.
For example, if you're working with a specific gas like oxygen (O2), you would enter its molar mass into the calculator, and it would return the specific gas constant for oxygen, which can then be used in thermodynamic calculations.