T-Test Calculator - T-Distribution Critical Values Table
What is a T-Test Calculator?
A T-Test Calculator is a statistical tool that helps determine if there’s a significant difference between the means of two groups. It’s based on the t-distribution, a probability distribution used when sample sizes are small, and the population standard deviation is unknown.
There are three main types of t-tests:
- One-sample t-test: Compares the sample mean to a known or hypothesized population mean.
- Two-sample t-test: Compares the means of two independent groups.
- Paired t-test: Compares means from the same group at two different times (before and after a treatment).
Why use a T-Test Calculator?
- Simplifies calculations: Avoids doing complex formulas by hand.
- Reduces human error: Ensures accurate results for statistical analysis.
- Determines significance: Helps assess whether observed differences are likely due to chance.
- Widely used: Essential in research, business, and medical studies.
How does a T-Test Calculator work?
- Input:
- Sample means
- Standard deviations
- Sample sizes
- Significance level (like 0.05)
- Calculation:
- Computes the t-statistic:
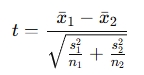
- Compares the t-statistic to critical values from the t-distribution table.
- Determines p-value and whether the result is statistically significant.
- Computes the t-statistic:
T-Distribution Critical Values Table:
The t-distribution table provides critical values based on:
- Degrees of freedom (df): df = n − 1 for one sample, or based on a more complex formula for two samples.
- Significance level (α): Common values are 0.05 (5%) or 0.01 (1%).
- Tails of the test: One-tailed or two-tailed tests.
When to use a T-Test Calculator?
- Comparing test scores: Checking if one class performed better than another.
- Evaluating treatments: Seeing if a new drug has a significant effect compared to a placebo.
- Business decisions: Comparing customer satisfaction before and after a policy change.
- Scientific research: Testing hypotheses with small sample sizes.