Thermal Conductivity Calculator
A Thermal Conductivity Calculator is a tool used to determine the thermal conductivity of a material. Thermal conductivity is a property that measures how well a material can conduct heat. It’s an essential factor in fields like material science, engineering, physics, and construction, where heat transfer is a critical consideration.
Why Thermal Conductivity Calculator is used:
It’s used because understanding how well a material can transfer heat helps in:
- Designing insulation materials: To prevent unwanted heat loss or gain in buildings, pipes, or equipment.
- Engineering applications: In systems like heat exchangers, radiators, or even electronic devices where managing heat is crucial.
- Material selection: Choosing the right material for specific applications, based on how it interacts with heat.
Thermal conductivity is often given in watts per meter Kelvin (W/m·K), and this calculator helps to quickly determine that value based on available data or properties of a material.
How Thermal Conductivity Calculator works:
The calculator typically uses the Fourier’s law of heat conduction formula, which states:
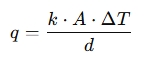
Where:
- q is the heat flow (in watts)
- k is the thermal conductivity of the material (the value we're solving for)
- A is the cross-sectional area through which heat is flowing
- TΔT is the temperature difference between the two sides of the material
- d is the thickness of the material
To calculate thermal conductivity, rearrange the formula to:
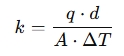
In the calculator, you’d input values for heat flow (q), area (A), temperature difference (ΔT), and thickness (d) to get the thermal conductivity (k).
When to use Thermal Conductivity Calculator:
You would use this calculator in situations like:
- Material selection: When designing products that need specific thermal properties, such as insulating materials in construction, thermal barriers in electronics, or coatings.
- Engineering and construction: To determine the heat flow through building materials or machinery parts.
- Thermal management: In electronics or mechanical systems, like cooling devices, where managing heat is vital.
- Laboratory testing: When experimenting with materials and trying to measure or compare their ability to conduct heat.
In short, it’s a handy tool whenever you need to understand how heat will move through a material, which is crucial for optimizing thermal performance in many industries.