Arrhenius Equation Calculator
What is an Arrhenius Equation Calculator?
An Arrhenius Equation Calculator is a tool used to calculate the rate constant (k) of a chemical reaction at a given temperature, based on the Arrhenius equation. The Arrhenius equation describes how the rate of a reaction changes with temperature, providing insight into the activation energy and how temperature affects reaction rates.
The Arrhenius equation is:
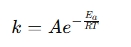
Where:
- k = Rate constant of the reaction
- A = Pre-exponential factor (frequency factor)
- Eₐ = Activation energy (in joules or kcal/mol)
- R = Universal gas constant (8.314 J/mol·K)
- T = Temperature (in Kelvin)
Why it's important:
The Arrhenius Equation is crucial in understanding how temperature and activation energy influence reaction rates. It is widely used in:
- Chemical Kinetics: To model and predict reaction rates at different temperatures.
- Materials Science: To understand how materials react under various temperature conditions.
- Pharmacology: In drug formulation, to predict the rate of chemical reactions (e.g., drug stability).
- Environmental Science: For studying the degradation of substances and reactions in nature at different temperatures.
By knowing the activation energy and pre-exponential factor, the Arrhenius equation helps in estimating how the reaction rate increases or decreases with temperature changes, which is essential for optimizing industrial processes, chemical production, and even understanding biological processes.
How it works:
The Arrhenius equation is used to calculate the rate constant (k) of a reaction, which is a key parameter in determining the speed at which a reaction occurs. It involves three main factors:
- Pre-exponential factor (A): This is a constant that represents the frequency of collisions between reactants and is typically determined experimentally.
- Activation energy (Eₐ): This is the energy barrier that must be overcome for the reaction to occur. Reactions with high activation energy proceed slowly, while those with low activation energy proceed more quickly.
- Temperature (T): The rate of reaction generally increases with an increase in temperature because higher temperatures provide the reactants with more energy to overcome the activation energy barrier.
Using the Arrhenius equation, you can determine the rate constant (k) at any given temperature, as long as you know the activation energy, pre-exponential factor, and temperature.
When it's used:
An Arrhenius Equation Calculator is used in various fields when:
- Studying chemical reactions: To model how the rate constant changes with temperature in laboratory experiments or industrial processes.
- Designing chemical processes: In chemical engineering, knowing the activation energy helps optimize reaction conditions, such as temperature and pressure, to maximize the efficiency of the process.
- Predicting reaction behavior: It can help predict the behavior of a reaction over a range of temperatures, which is useful for research, development, and quality control in industries like pharmaceuticals, manufacturing, and food processing.
- Environmental Science: To study how temperature influences the rate of natural processes like the degradation of pollutants or the cycling of nutrients in ecosystems.
Arrhenius Equation Calculator:
An Arrhenius Equation Calculator typically allows you to input the following parameters:
- Pre-exponential factor (A): Often provided from experimental data.
- Activation energy (Eₐ): The energy required for the reaction to proceed, usually given in joules or kcal/mol.
- Temperature (T): The temperature at which the reaction is occurring, given in Kelvin.
The calculator then calculates the rate constant (k) of the reaction at the given temperature.
For example:
- If you have an activation energy of 50 kJ/mol, a pre-exponential factor of 1.0×1013 s−1, and a temperature of 300 K, the calculator will provide the rate constant (k) at that temperature.
Example Use Case:
- In pharmaceutical industries, when formulating a drug, knowing the activation energy and temperature helps predict how quickly the drug breaks down over time, allowing for better shelf life predictions.
- In chemical manufacturing, the calculator helps optimize reaction conditions (like temperature) to improve product yield and reaction efficiency.
In short, an Arrhenius Equation Calculator simplifies the process of calculating reaction rates at different temperatures, which is essential for various scientific, industrial, and environmental applications.