Combined Gas Law Calculator
What is the Combined Gas Law?
The Combined Gas Law is a formula that combines Boyle's Law, Charles' Law, and Avogadro's Law into one equation, allowing you to calculate the relationship between the pressure, volume, and temperature of a gas when the amount of gas (number of moles) remains constant.
The equation is:
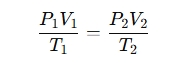
Where:
P₁ = Initial pressure
V₁ = Initial volume
T₁ = Initial temperature (in Kelvin)
P₂ = Final pressure
V₂ = Final volume
T₂ = Final temperature (in Kelvin)
Why it's important:
The Combined Gas Law is helpful because it allows you to relate the pressure, volume, and temperature of a gas without needing to know the number of moles. This is especially useful when you have a gas sample where the number of particles is constant, and you need to calculate how one property changes when the others are altered.
How it works:
This equation combines three gas laws into one, meaning it's applicable when:
Pressure and volume can change.
Temperature can change.
The amount of gas remains constant.
When you change any of the variables (P, V, or T), the others adjust according to the Combined Gas Law.
For example:
If the pressure increases, the volume decreases (at constant temperature).
If the temperature increases, the volume also increases (at constant pressure).
When it's used:
The Combined Gas Law is useful when:
You're dealing with a fixed amount of gas, and any two of the properties (pressure, volume, temperature) change.
You need to predict how a gas will behave under different conditions (like temperature or pressure changes).
Combined Gas Law Calculator:
A Combined Gas Law Calculator allows you to quickly find the missing variable (pressure, volume, or temperature) when the other variables are known.
Input: You'd input initial values for pressure, volume, and temperature, along with the final values for any of these variables (except for the one you're solving for).
Output: The calculator will provide the value of the missing property.
For example, if you know the initial and final pressures and temperatures of a gas, the calculator can find the final volume.
It's used in situations like:
Predicting the behavior of a gas in an engine or industrial process where conditions change, but the gas amount remains constant.
Understanding how gases behave when they're heated or cooled under varying pressures.