Doppler Effect Wavelength Front Calculator
A Doppler Effect Wavelength Front Calculator is a tool used to calculate the change in the wavelength of a wave (such as sound, light, or electromagnetic waves) due to the relative motion between the source of the wave and the observer. This phenomenon is known as the Doppler Effect and it affects the frequency and wavelength of the wave depending on whether the source is moving towards or away from the observer.
What is the Doppler Effect?
The Doppler Effect describes the change in frequency (or wavelength) of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the wave source. It occurs for all types of waves, including sound, light, and radio waves, and is most commonly heard in the context of sound (e.g., a passing siren whose pitch changes as it moves towards or away from an observer).
- Approaching Source: If the wave source is moving towards the observer, the wavelengths are compressed, leading to an increase in frequency (higher pitch or blue-shifting in the case of light).
- Receding Source: If the source is moving away from the observer, the wavelengths are stretched, leading to a decrease in frequency (lower pitch or red-shifting in the case of light).
Why use a Doppler Effect Wavelength Front Calculator?
The Doppler Effect Wavelength Front Calculator helps in accurately predicting the change in wavelength or frequency that an observer perceives when there is relative motion between the source and the observer. It is particularly useful in:
- Astronomy: To determine the movement of stars, galaxies, and other celestial objects (e.g., redshift or blueshift).
- Radar and sonar systems: To measure speed and direction of moving objects.
- Communication systems: To predict how the movement of a transmitter or receiver can affect signal frequency or wavelength.
- Acoustics and audio: To model the change in sound pitch as moving sound sources approach or recede from an observer.
How does a Doppler Effect Wavelength Front Calculator work?
The calculator uses the Doppler Effect equations that relate the speed of the source, the speed of the observer, and the speed of the wave to the perceived frequency or wavelength.
For sound waves in air, the equation for the Doppler effect is:
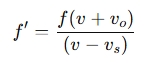
Where:
- f ′ = observed frequency
- f = emitted frequency (frequency of the source)
- v = speed of sound in the medium
- vo = speed of the observer (positive if moving towards the source)
- vs = speed of the source (positive if moving towards the observer)
For light waves, the relativistic Doppler effect formula can be used:
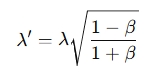
Where:
- λ ′ = observed wavelength
- λ = emitted wavelength
- β= v / c (the ratio of the source's velocity to the speed of light)
These equations can be simplified depending on the type of wave and the scenario.
When to use a Doppler Effect Wavelength Front Calculator?
A Doppler Effect Wavelength Front Calculator is used when:
- Observing moving objects: When the source of waves (sound, light, etc.) is in motion relative to an observer, and you need to calculate how the wavelength or frequency changes.
- Analyzing radar and sonar signals: For measuring the speed of moving objects, such as vehicles, airplanes, or submarines.
- Studying astronomical phenomena: To analyze the motion of celestial bodies based on the redshift or blueshift of light waves.
- Designing communication systems: To model and correct for the effects of relative motion between transmitters and receivers in satellite or mobile communication systems.
In short, the Doppler Effect Wavelength Front Calculator is an essential tool for applications that involve wave behavior in moving systems, enabling accurate predictions of frequency and wavelength shifts due to motion.