Power Harmonics Calculator
What is a Power Harmonics Calculator?
A Power Harmonics Calculator helps analyze the presence of harmonic distortion in electrical power systems. Harmonics are unwanted multiples of the fundamental frequency (usually 50 or 60 Hz), caused by nonlinear loads such as variable-speed drives, fluorescent lights, and computers. These harmonics can affect the quality of power, cause overheating, and reduce the efficiency of electrical equipment.
Why Use a Power Harmonics Calculator?
- Improve power quality by identifying harmonic distortions in the system.
- Optimize energy consumption by mitigating the effects of harmonics on electrical devices.
- Prevent equipment damage by detecting excessive harmonic levels that can lead to overheating, equipment failure, or reduced lifespan.
- Compliance with standards: Many utilities and industries have regulations on harmonic distortion levels (e.g., IEEE 519 standards).
How to Calculate Power Harmonics?
The basic method for calculating harmonics involves measuring the total harmonic distortion (THD) and individual harmonic components. Here’s how it’s typically done:
Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) Formula:
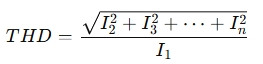
Where:
- THD = Total harmonic distortion (expressed as a percentage)
- I_1 = Fundamental current (or voltage)
- I_2, I_3, ..., I_n = Harmonic currents (or voltages) of the 2nd, 3rd, ..., nth harmonics
Individual Harmonic Calculation:
For each harmonic (e.g., 2nd harmonic, 3rd harmonic, etc.), you can calculate the current or voltage distortion at that frequency using Fourier analysis or digital signal processing (DSP) methods.
Harmonic Power Calculation:
If power is being analyzed for harmonics, it can be broken down into:
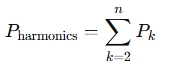
Where:
- P_k = Power of the k-th harmonic.
When to Use a Power Harmonics Calculator?
- Power quality analysis: To measure and mitigate harmonic distortion in electrical systems.
- Energy efficiency improvements: In systems with non-linear loads, like industrial machines or data centers.
- Equipment protection: To prevent overheating or premature failure of electrical equipment.
- Compliance checks: To ensure your system meets local or international power quality standards (e.g., IEEE 519).