Kinematic Viscosity Calculator
What is a Kinematic Viscosity Calculator?
A kinematic viscosity calculator helps determine the kinematic viscosity (ν\nu ν) of a fluid, which is the ratio of its dynamic viscosity (μ\mu μ) to its density (ρ\rho ρ). It is expressed as:
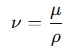
Where:
- ν = Kinematic viscosity (m²/s or cSt)
- μ = Dynamic viscosity (Pa·s or N·s/m²)
- ρ = Density of the fluid (kg/m³)
Kinematic viscosity describes a fluid’s resistance to flow under gravity, commonly measured in Stokes (St) or centiStokes (cSt):
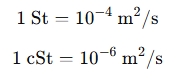
Why Use a Kinematic Viscosity Calculator?
- Engineering & Mechanics: Determines lubrication efficiency in engines and machines.
- Petroleum Industry: Essential for classifying oils and fuels (e.g., SAE oil grades).
- Chemical Processing: Helps design pipelines and mixing processes.
- Aerospace & Marine: Ensures proper fuel and hydraulic fluid flow.
- Food & Beverage Industry: Used in processing oils, syrups, and dairy products.
How to Use the Calculator?
- Obtain dynamic viscosity (μ) from lab tests or manufacturer data.
- Measure fluid density (ρ) at the same temperature.
- Use the formula ν= μ / ρ to calculate kinematic viscosity.
- Convert units if needed, e.g., from m²/s to cSt.
For experimental measurement, kinematic viscosity can also be found using a capillary viscometer (like an Ostwald or Ubbelohde viscometer), where:
ν = C × t- C = Calibration constant of the viscometer
- t = Time taken for fluid to flow through the capillary (seconds)
When is Kinematic Viscosity Calculation Used?
- Before selecting lubricants: Ensuring proper lubrication for engines and gears.
- In fluid flow analysis: Designing hydraulic and cooling systems.
- For fuel and oil testing: Meeting quality standards like ASTM D445.
- In aerodynamics and meteorology: Studying air and water movement.
- In chemical processing plants: Optimizing mixing, transport, and reactions.