Leaf Spring Rate Calculation
What is Leaf Spring Rate Calculation?
Leaf spring rate calculation determines the stiffness (spring rate) of a leaf spring, which is a crucial component in suspension systems for vehicles, trucks, and trailers. The spring rate measures how much force (in pounds or Newtons) is required to deflect the spring by a given distance (typically inches or millimeters).
Why is Leaf Spring Rate Calculation Important?
- Vehicle Load Handling – Ensures the suspension supports the weight of the vehicle and cargo.
- Ride Comfort – Balances stiffness and flexibility for a smoother ride.
- Performance & Stability – Optimizes handling and stability under different load conditions.
- Suspension Tuning – Helps engineers design springs suited for specific applications like off-road vehicles, racing cars, or heavy-duty trucks.
How to Calculate Leaf Spring Rate?
The spring rate ( k) for a leaf spring can be calculated using the following formula:
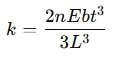
Where:
- k = Spring rate (force per unit deflection, e.g., N/mm or lb/in)
- n = Number of effective leaves (depends on leaf configuration)
- E = Modulus of elasticity of the material (e.g., for steel, E≈200 GPa)
- b = Width of a single leaf (mm or inches)
- t = Thickness of a single leaf (mm or inches)
- L = Half the length of the spring (measured from the center bolt to the eye, in mm or inches)
When is Leaf Spring Rate Calculation Used?
- During vehicle suspension design and development.
- When modifying or upgrading a vehicle’s suspension system.
- To troubleshoot or replace worn-out leaf springs in trucks, trailers, or off-road vehicles.
- In custom fabrication for race cars or heavy-duty applications.