Log Mean Temperature Difference Calculator
What is a Log Mean Temperature Difference (LMTD) Calculator?
A Log Mean Temperature Difference (LMTD) calculator is a tool used to determine the average temperature difference between two fluids exchanging heat in a heat exchanger — like in condensers, boilers, and radiators. LMTD provides a more accurate measurement when temperatures change along the heat exchanger’s length.
The LMTD formula is:
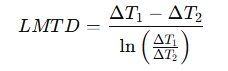
Where:
- ΔT1 = Temperature difference at one end of the exchanger
- ΔT2 = Temperature difference at the other end
Why use an LMTD Calculator?
- Accurate heat transfer calculation: Accounts for changing temperature differences along the exchanger.
- Design efficiency: Helps size heat exchangers by ensuring the right surface area and flow rates.
- Performance evaluation: Checks if the heat exchanger is working efficiently.
- Saves time: Automates a complex formula and reduces calculation errors.
How does it work?
- Input hot fluid temperatures: Inlet and outlet temperatures (Th1 and Th2).
- Input cold fluid temperatures: Inlet and outlet temperatures (Tc1 and Tc2).
- Calculate temperature differences: ΔT1=Th1−Tc1,ΔT2=Th2−Tc2
- Apply the LMTD formula: Calculate the log mean temperature difference.
- Use the result: Apply LMTD in the heat transfer equation Q=UA⋅LMTD, where is heat transfer rate, is heat transfer coefficient, and A is surface area.
When do you use it?
- Designing heat exchangers: To ensure the right heat transfer capacity.
- Analyzing system performance: Checking efficiency in HVAC systems, boilers, and radiators.
- Optimizing industrial processes: In power plants, refineries, and chemical production.
- Research and engineering: For heat transfer studies and experiments.