Flow calculator
What is a Flow Calculator?
A Flow Calculator is a tool used to calculate the flow rate of liquids or gases through pipes, channels, or other systems. Flow refers to the volume of fluid passing through a specific area per unit of time and can be measured in units like liters per second (L/s), cubic meters per hour (m³/h), or gallons per minute (GPM). The calculator can be used for a variety of applications, from industrial fluid transport to water system design.
Why Use a Flow Calculator?
- Optimize system design: Ensure that pipes, pumps, and valves are properly sized for fluid transport.
- Monitor system performance: Measure actual flow rates to ensure that systems are functioning efficiently.
- Troubleshoot issues: Identify blockages, leaks, or malfunctions by checking if flow rates are within expected ranges.
- Energy efficiency: In pumping systems, minimizing flow rate can reduce energy consumption and costs.
How to Calculate Flow?
There are various methods for calculating flow depending on the type of system and available measurements. Below are common formulas:
For Fluid Flow in Pipes (using the Continuity Equation):
Q = A × VWhere:
- Q = Flow rate (m³/s, L/s, GPM)
- A = Cross-sectional area of the pipe (m², cm²)
- V = Velocity of the fluid (m/s, cm/s, ft/s)
For Fluid Flow Using Bernoulli’s Equation (Ideal Fluids):
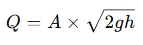
Where:
- Q = Flow rate (m³/s)
- A = Cross-sectional area of the pipe (m²)
- g = Acceleration due to gravity (9.81 m/s²)
- h = Height difference (meters)
For Flow in Open Channels (using Manning’s Equation):
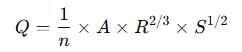
Where:
- Q = Flow rate (m³/s)
- n = Manning’s roughness coefficient (depends on the channel surface)
- A = Cross-sectional area of flow (m²)
- R = Hydraulic radius (m), calculated as A / P, where P is the wetted perimeter
- S = Slope of the channel (dimensionless)
When to Use a Flow Calculator?
- Designing pipelines or plumbing systems: Ensure the correct pipe size and flow capacity for fluid transport.
- Water distribution systems: Calculate flow rates in irrigation, sewage, and municipal water systems.
- Pumping systems: Monitor and optimize pump performance, ensuring that pumps are running efficiently at the desired flow rates.
- Environmental engineering: Assess flow in rivers, streams, and wastewater treatment facilities.
- HVAC systems: Determine the airflow rate in ventilation and air conditioning systems.