Radar Range Calculator
What is a Radar Range Calculator?
A Radar Range Calculator is a tool used to determine the maximum detection range of a radar system based on its power, antenna characteristics, target properties, and environmental factors. It is based on the Radar Range Equation, which calculates how far a radar can detect a target.
The most common formula for radar range is:
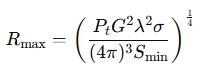
Where:
- Rmax = Maximum radar detection range (m)
- Pt= Transmitted power (W)
- G = Antenna gain (unitless)
- λ = Wavelength of the radar signal (m)
- σ = Radar cross-section of the target (m²)
- Smin = Minimum detectable signal power (W)
Why Use a Radar Range Calculator?
- Military & Defense: Determines how far a radar system can detect aircraft, missiles, or ships.
- Aviation & Air Traffic Control: Helps ensure safe airspace monitoring.
- Weather Forecasting: Used in meteorological radars for storm detection.
- Automotive Industry: Calculates the range of radar in self-driving cars.
- Space & Astronomy: Used in planetary radars to detect objects in space.
How to Use the Calculator?
-
Input radar parameters:
- Transmit power (Pt)
- Antenna gain (G)
- Wavelength (λ), based on radar frequency
- Target radar cross-section (σ)
- Minimum detectable signal power (Smin)
-
Apply the Radar Range Equation to find Rmax .
-
Convert units if necessary:
- Wavelength λ\lambda λ can be found using λ=c / f , where cc c is the speed of light (3 × 10⁸ m/s) and f is frequency (Hz).
When is a Radar Range Calculation Used?
- Before designing a radar system: Ensures the system meets detection requirements.
- For military applications: Determines the range of surveillance and tracking radars.
- In airport surveillance: Calculates the effective coverage of radar systems for air traffic control.
- For weather radar systems: Evaluates how far radar can detect rain, storms, and tornadoes.
- For autonomous vehicles: Helps design short-range and long-range automotive radar.